
If you’re a beginner, hosting a website might seem like a huge deal. It’s really not. In fact, once you have done it, you’ll wonder what you were worried about!
A simple Google search will lead you to thousands of articles and videos, each with different ideas on how to host a website. There is so much information out there that you could quickly suffer from information overload.
Fear not, for, in this guide, we’ll cover essential aspects of hosting your website.
I’ll walk you through the entire process of hosting your own website on a popular hosting platform.
We’ll discuss choosing a host, what to look for and briefly outline how you set everything up.
By the end of this post, you’ll understand everything you need to know about hosting a WordPress website and how to select a host.
What Is Web Hosting?
Let’s start with the most basic question – what is web hosting and why do you need it?
I’ll answer the question with an example.
Let’s say you’re opening a store. For that, you need a brick and mortar space where you can display all your products and greet your customers. You often start by renting a space and then perhaps purchase one as your business grows.
The same happens when you host your website. You rent space on a web server from a web hosting provider.
Web servers come with the functions and connectivity you need for your website to be accessible from the internet.
You install WordPress to enable basic functionality and then upload all your website files to the server so everything can work as you designed it.
What Are Domain Names?
A domain name is the address that visitors type into their browser. Do you see in the URL box above in your browser, the ‘www.wpcrafter.com’?
That’s my domain name.
Choosing a domain name requires some planning because it represents your business on the internet. You want it to be descriptive and represent your business in the right way.
If you need to explore the idea in detail, here’s a detailed guide to domain names.
Windows Servers vs Linux Servers
When browsing for web hosting, you’d come across both Linux and Windows servers. This isn’t a vital question as both types of server get the job done but I wanted to cover it briefly for completeness.
I recommend you go with Linux hosting because it dominates the web hosting industry. It also supports my favorite control panel, cPanel, which Windows does not.
If you were an experienced developer or knew that you needed MS-SQL databases, ASP.NET, or .NET Core for your website, you would use Windows.
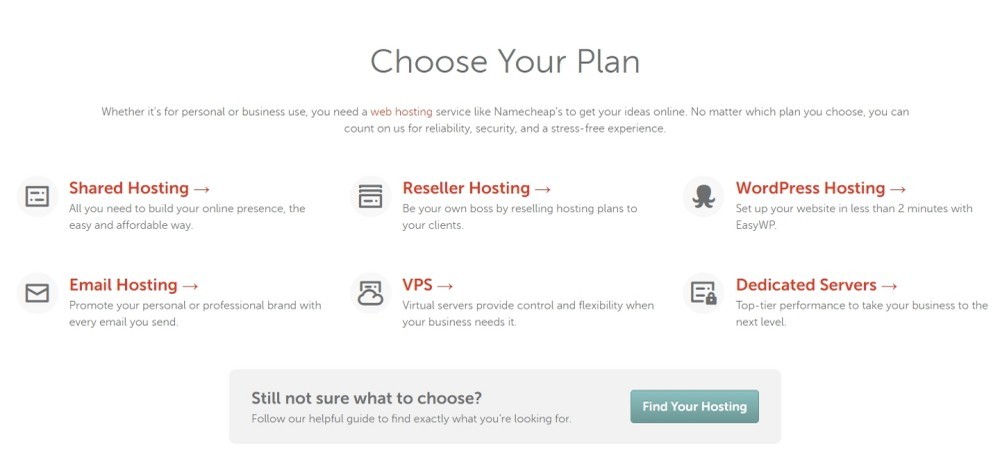
Types of Hosting Solutions
Hosting solutions come in several flavors, each catering to a specific audience with particular requirements.
It might help to understand the pros and cons of these hosting types to find out what fits your requirements.
Shared Hosting
Shared hosting, as the name implies, is a solution where several (hundred or thousand) websites are hosted on a single web server.
All websites share server resources, which is why shared hosting is so cheap. Often businesses host their websites and blogs on a shared hosting server and then scale up as they outgrow the solution.
Shared hosting can cost between $3 to $9 a month.
Pros of shared hosting:
- Shared hosting is often the most competitively priced solution
- You don’t have to manage the server hardware or invest time in server administration
- No server setup is required. Just upload your website and go
Cons of shared hosting:
- You cannot change the settings and software on the server
- Server performance will vary as all the websites hosted on the server compete for the same resources
- If one website on a shared hosting gets compromised, chances are all websites hosted on that server would also be compromised
Virtual Private Servers (VPS)
VPS hosting is an interesting concept. Its physical server is portioned off into several virtual servers, complete with a dedicated OS and allocated server resources. So, in essence, it’s shared hosting but each portion is a distinct server.
A VPS works as a dedicated server that you control through a hosting panel.
The server resource allocation is also much more generous than shared hosting. That means a VPS server could handle more traffic and requests than a shared hosting server.
Many growing business websites, eCommerce stores, and popular blogs prefer VPS because these solutions offer more flexibility than shared servers.
The price for VPS hosting starts from around $35 a month.
Pros of VPS hosting:
- You can scale a VPS solution by purchasing additional resources when you need them
- You get administrator access to your virtual server and can install your own software
- Security is much better than shared hosting because each virtual server is compartmentalized. As such, there is little impact if another website is compromised
Cons of VPS hosting:
- You need to configure and manage your VPS server yourself or pay for a managed VPS
- Once scaled up, downscaling a VPS is often costly or impossible
- You still have to manage resources because, under the hood, it’s still a shared hosting solution
Dedicated Hosting
Dedicated hosting is the Rolls Royce of hosting solutions, and just as expensive!
With dedicated hosting, you get a server dedicated to yourself. You get all the server resources and full access to the server with nominal restrictions. You start by installing an OS of your choice and then set up the server software as you wish.
All this power comes at a cost. Both in terms of skills and investment.
You need the technical skills to set up and manage dedicated servers. It also requires continuous attention to server performance, security, and software updates.
As you’re essentially renting your own server, it requires quite the cash investment too.
Dedicated hosting solutions are used by huge eCommerce stores, enterprise-level business websites, and any website that needs to serve a large number of visitors simultaneously.
Dedicated hosting offers the best in terms of performance and security but comes at a high price.
Dedicated hosting would typically start at around $80 per month.
Pros of dedicated hosting:
- Dedicated hosting is incredibly flexible. You can set up any type of software environment you need for your business
- All server resources are dedicated to your website
- With the right setup and maintenance, you can get extreme performance out of your dedicated server
Cons of dedicated hosting:
- Dedicated servers have high ownership costs
- You need to have server management skills or know somebody who does
- Scaling your current dedicated server is often costlier than getting a new dedicated server
Managed Cloud Hosting
Managed cloud hosting is a hybrid option that uses virtual servers. The hosting provider manages everything from server setup to maintenance and you can do anything you like with the resources.
All you see is a hosting panel where you upload your website and make it available to the world.
In many cases, you don’t interact with the server at all. You just see the software layer where your WordPress website resides.
This is an ideal solution for users who don’t want to deal with server maintenance. You get an account with a managed cloud hosting provider and leave everything server-related (including security, updates, and backup) to the service provider.
Managed cloud hosting services generally start from $10 a month.
Pros of managed cloud hosting:
- Preconfigured servers that help you focus on your business
- You generally pay only for the resources you consume in a billing cycle (usually monthly)
- Scaling managed hosting service is as often as simple as moving a slider in the panel
Cons of managed cloud hosting:
- Managed services are usually more expensive than other hosting solutions with similar specifications
- You need to remain mindful of website security and maintenance
- Every provider has got their own estimation of server resources you’d need. This means you might need to pay for additional resources

Things to Consider When Choosing a Hosting Provider
Choosing a hosting provider is a serious business. You want one that offers the best combination of hosting type and server resources that fits your budget.
Since there are many hosting service providers on the market, choosing the perfect fit often requires investing a lot of time in your evaluation.
I recommend using the following factors when considering providers:
Average Uptime
Uptime is a measure of how long your website (and the server) remains available to visitors. This is the basic parameter that determines the performance of the hosting service provider.
Remember that every minute your website is down and unavailable, you’re losing credibility and revenue!
Average uptime is measured over a specific period of time (usually a month). Many hosts ensure 99.95% uptime with top-of-the-line providers going up to 99.99%.
This value is usually displayed prominently on the provider’s website. However, you should verify the claim by monitoring the uptime with third-party server monitoring tools such as Pingdom.
If the uptime is lower than the host’s guarantee, inform them so that they could rectify the issue from their end. If the issue persists, it’s time to look for a new host.
Server Speed and Page Load Time
Google considers page load speed as an important ranking factor. The speed of the server and how fast it serves website content in response to the visitors’ requests have a serious impact on that.
When evaluating server speed, find out the average Time to First Byte (TTFB) of the host. This measures server responsiveness. Google recommends a TTFB of 200ms, with 500ms being the limit.
If the host’s TTFB is slower than that, you may want to look elsewhere.
Security
Server security is a no-brainer in these times of cyber crimes and security breaches.
At the minimum, you should make sure that a host offers the following:
- Server level firewalls and Intruder Detection Systems (IDS)
- Protection against bots and Denial of Service attacks (DDoS)
- Regular patching for the OS and server software
- Active server monitoring and regular reporting
You should also check if the host offers SSL certificates. These certificates are essential for authenticating the website’s identity and help set up an encrypted connection between the server and the visitors’ browsers.
In addition, look for data protection and processing agreements to make sure your server remains GDPR compliant if you’re based or do business in the EU.
Customer Support
When the worst happens, you will benefit from competent customer support that has the experience and expertise to understand the underlying issues. Support that takes ownership of issues and works hard to rectify them.
It’s worth checking if you can reach customer support via phone, chat, or email. Ideally, support should respond within a couple of hours (less, in the case of a full outage).
The best way of finding out the quality of technical support is to read reviews and check feedback websites.

Bandwidth and Storage Limits
Hosting providers, particularly shared and VPS hosting providers, can sometimes place upper limits on bandwidth and disk space that your website can use.
Disk space is a physical limitation, so is understandable. Bandwidth is not, which is why it’s difficult to recommend using a web host that has bandwidth or visitor limits.
If you hit these limits, you can either buy additional resources or wait for them to be replenished at the start of the next month.
When considering a provider, look for unlimited bandwidth and generous storage. There is too much competition out there to settle for anything less.
Datacenter Location
Some web hosts offer multiple datacenter locations where you can place your server.
This is an important decision if you are targeting a specific geographical location such as a city or a country. You need to find a hosting provider that maintains data centers in or near that location.
While not vital, it can improve response times for those visitors and have a minor SEO benefit too.
Shorter distances between the server and visitor means faster response times, which is what everyone wants.
Backups
Taking backups of website data is your responsibility since you own that data. However, good hosting providers usually provide their own paid or free backup services.
The duration for which they keep the backup can vary from 10 to 30 days. In the case of VPS or cloud hosting, providers generally offer a server-wide backup that saves the data of all your websites hosted on their server.
If you use WordPress, you can configure your own software backup solution but it’s good to have options.
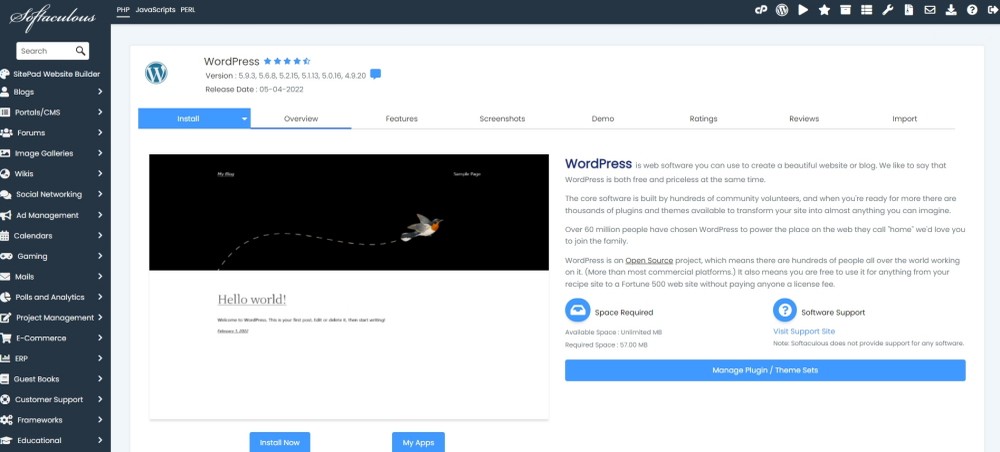
Optional Features
In addition to the above features, you could also consider the following options.
They are not critical, but they can save time and help you better manage your business.
Click WordPress installation
Installing WordPress can be tedious if you have to do it manually. To save time, look for hosts that offer a 1-click WordPress installation feature that sets up a WordPress website, or one that does it all for you.
CDN Availability
Regardless of where they come from, your visitors want your website to work quickly.
For this, you need a Content Distribution Network, or CDN. A CDN is a network of servers that stores a copy of your website on each server (also known as nodes) and selects the server closest to the visitor.
Look for a host that offers simple integration of a reliable CDN provider with their hosting service.
Server Control Panel
Almost every hosting provider offers some sort of server and website control panel.
While cPanel is a popular choice, you would find several types of these panels. I recommend you try a demo or check out the documentation to see if you feel comfortable using it.
How to Host Your Website
Whatever hosting you choose, the process of hosting your website is pretty similar. It involves the following steps.
To illustrate the process, I’ll use a shared hosting provider.
Step 1: Buy the Domain
The first step of the process is selecting a domain name for your website.
Often, you will have some domain names shortlisted beforehand. Check whether the domain name you need is available before committing.
In addition to the actual domain name, you need to give careful thought to the top-level domain (TLD) – the part that comes after the domain name.
You can pick from the generic TLD (usually, COM, ORG, NET, and BIZ) or country-specific TLD (such as US, EU).
While COM is the most common on the internet, you can often find your preferred domain name with ORG or NET. If these are also taken, try the country-specific TLD.
To check if a domain name is available, simply enter it in the search box and the system will tell if it’s available or taken.
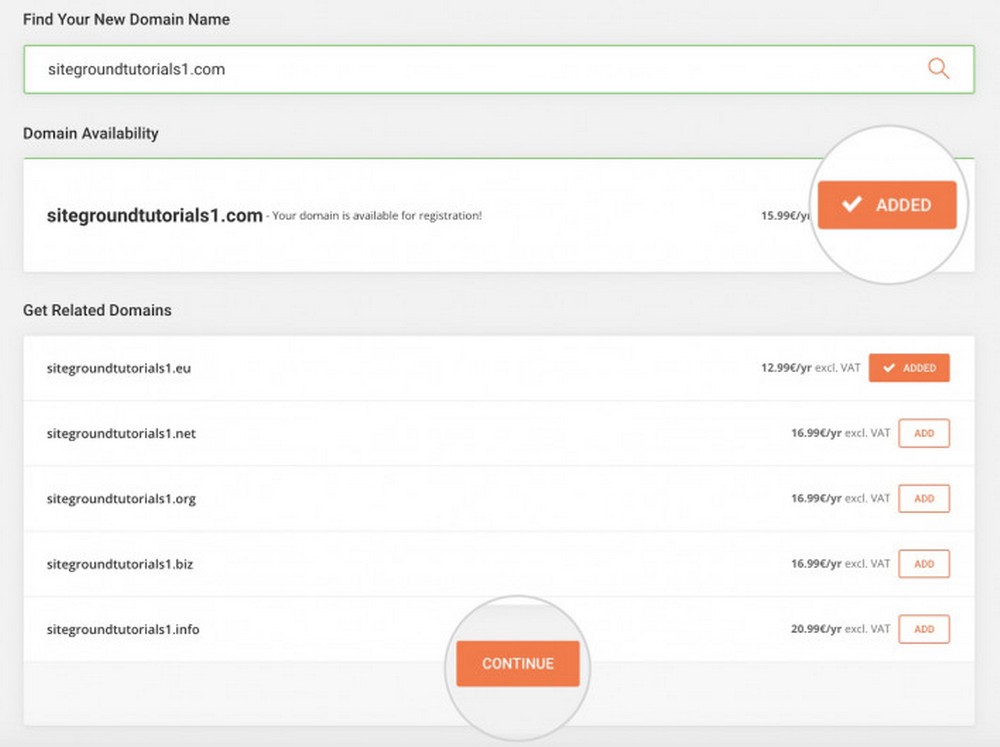
If available, select it to continue to the next step. Otherwise, select one of the available variations or repeat the process with the next name on your list.
Step 2: Set Up Your WordPress Website
Now that you have a domain name, the next step is to set up your WordPress website.
Almost all hosting providers offer a simple process of setting up your WordPress website. Usually, you need to go through just two or three steps to finalize the process.
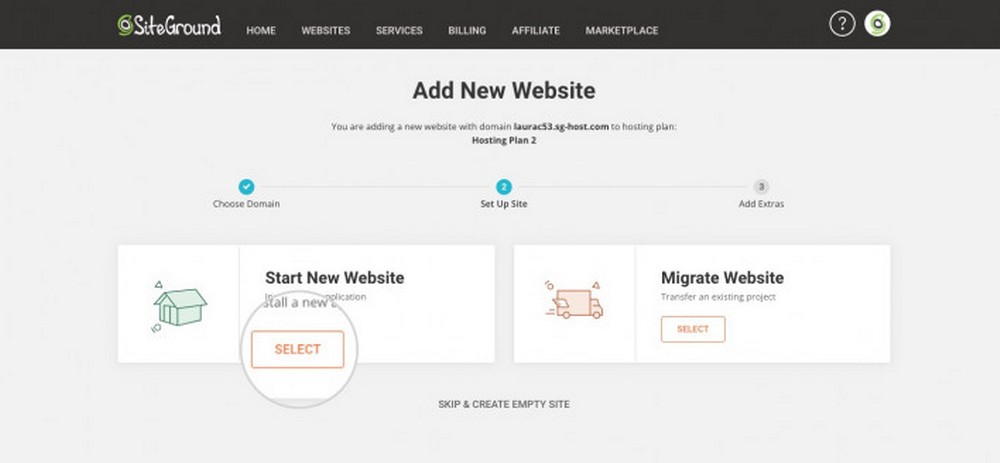
Opt to Set up a New Website
You often get the option to set up a new website or migrate your existing website to your new hosting provider.
Since we are setting up a new website, we’ll go with that option.
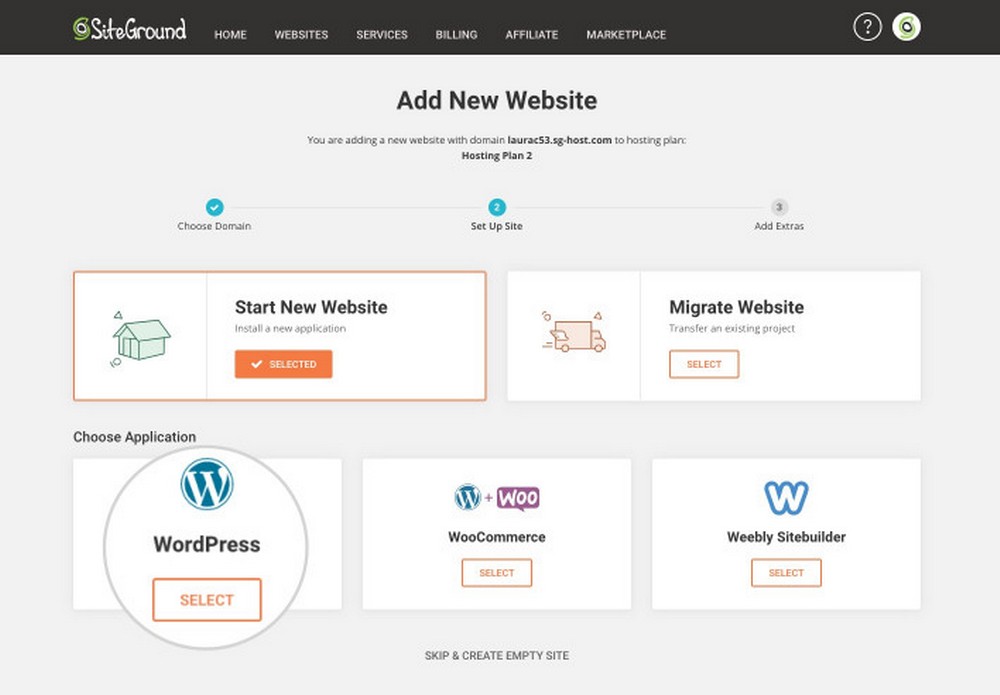
Select WordPress as Your Application
WordPress is so popular that almost every hosting provider from shared to the managed cloud offers a 1-click WordPress setup.
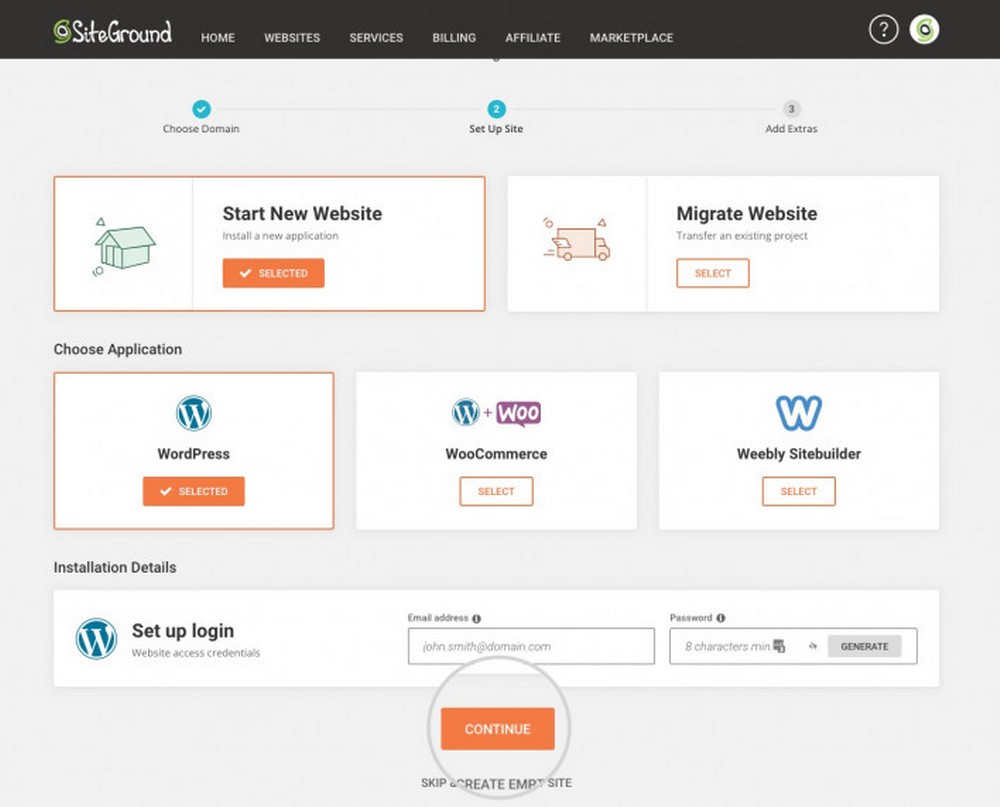
The process simply requires an email address and password.
Choose an email address you can monitor from anywhere and a password that’s complex but easy to remember. You’ll need both of them to log into your website.
Depending on the host, the process might end at this point, or you may be asked to install additional components.
Finalize the steps to close the setup wizard.
Within minutes, your new website would be ready to use!
What’s Next for Your Website?
Once WordPress has been installed and your website set up, you can change the theme, install and activate your preferred plugins, and upload your content. Setting up a website is very straightforward, but if you don’t have the time or the experience to do it yourself, consider using a web design company to do it for you.
This will obviously take some time but you can do whatever you like once the site is set up. You can add a theme, add some plugins and configure your site however you like!
Conclusion
Hosting your website is the first step in launching your online presence. Finding the right hosting solution is a process that takes time, effort and research, but isn’t difficult.
Choosing a reliable hosting provider is essential for small businesses; here is everything top web hosting sites should do, head over to their site to know more.
We hope that after reading this guide, you have a clear understanding of the type of hosting solutions out there, and what factors to consider when shortlisting a host.
We hope you also have an idea of how simple it is to set up WordPress and install a website. It really is easy once you try!
Did this guide help you understand web hosting a little better? Did you find value in it? Let me know below!
This information is more helpful and platform for building, hosting website